Helium-Neon Gas Laser
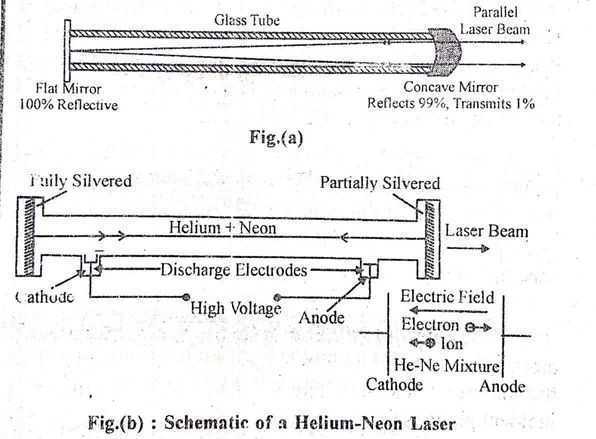
He-Ne Gas laser consists of a narrow discharge tube of bore glass or quartz of length 10 to 100 cm with a diameter of the order of 5mm to 10mm.He-Ne Laser construction
- The tube is Filled With a mixture of helium and neon gases, approximately in the ratio, 85 % a helium and 15% neon, contained at low pressure (typically ~2-3 torr). At each end of the tube, there are electrical connections, referred to as electrodes.
- The energy or pump supply of the laser is provided by a discharge of around a thousand V through an anode and cathode at every finish of the glass tube.
- The positive high voltage is connected to the anode and cathode, lS took at ground potential.
- The anode consists of a metal pin inserted through the glass so that one end extends into the gas region of the tube and the other is connected to the power supply as‘ shown‘ in fig. (b).
- The laser tube is enclosed between a plane, high-reflecting mirror at one end, and a concave output coupler mirror of approximately 1% transmission at the other end as shown in fig. (a).
- These mirrors might be flat, however, this needs nice precision in alignment, therefore the common laboratory He-Ne laser is factory-made with the semi-confocal mirror arrangement.
- The spacing between the mirrors is taken equal to an integral multiple of half wavelength of laser light.
He Ne Laser Working
- The laser process in a He-Ne laser starts with the collision of electrons with the helium atoms in the gas by the electrical discharge.
- This electric discharge excites helium from the ground state, to the long-lived, metastable excited states.
- The collision of the excited helium atoms with the ground-state neon atoms results in the transfer of energy to the neon atoms, exciting them into the 25 and 33 states.
- The excess energy in a helium atom is transferred during a collision to a neon atom.
- Helium is used because, it possesses an exciting state very close to the upper (35) level in neon and this helium level is metastable, meaning it has a very long lifetime (as one of the exciting levels of helium at 20.61 eV is very close to a level in neon at 20.66 eV, so close in fact that upon the evolution of helium and a neon atom, the energy can be transferred from the helium t0 the neon atom).
- The helium excited state is readily produced by electrical discharge and such a large population of excited helium atoms can be created that a population inversion of neon atom sean he made.
- This process is given by the reaction equation :
He* + Ne --> He + Ne* +AE
- where (*) represents an excited state, and AB is the small energy difference between the energy states of the two atoms, of the order of 0.05 eV.
- To ensure the emission processes exceed the absorption process, there must be a population inversion, namely an excess of excited states.
- The number of neon atoms entering the exciting states will increase as further collisions between element and neon atoms happens, causing a population inversion between them. neon 3s and twenty-three, and 3p and 2p states.
Role of He in He-Ne Gas
The role of helium gas in the laser tube is to provide the pumping medium to neon atom to attain the necessary population inversion for laser action.