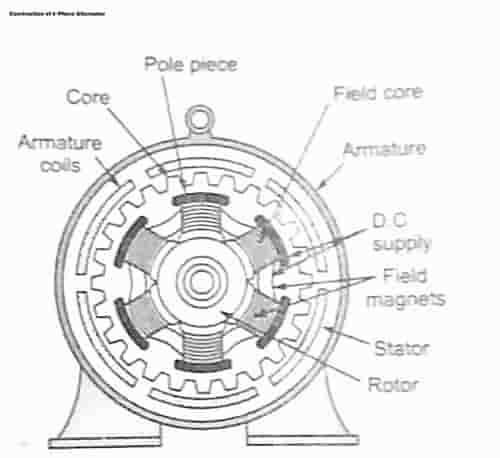
Construction of 3-Phase Alternator
A 3-Phase alternator has 3-stage winding on the stator and a d.c. the field winding on the rotor.1. Stator
- It is the stationary piece of the machine and is developed of sheet-steel overlays having openings on its inward outskirts.
- A 3-stage winding is put in these spaces and fills in as the armature winding of the alternator.
- The armature winding is constantly associated star and the unbiased is associated with the ground.
2. Rotor
- The rotor conveys a field winding which is provided with direct current through two slip rings by a different d.c. source.
- This d.c. source (called exciter) is commonly a little d.c. shunt or compound generator mounted on the pole of the alternator.
Rotor development is of two types, to be specific ;
(1) Salient (or anticipating) post type
(2) Non- Salient (or cylindrical) shaft type
(1) Salient post type
- In this sort, remarkable or anticipating poles are mounted on an expansive round steel outline which is fixed to the pole of the alternator as appeared in Fig. 22.2.
- The individual field pole windings are associated in an arrangement so that when the field winding is invigorated by the d.c. exciter, adjoining poles have inverse polarities.
Slow and medium-speed alternators (120-400 r.p.m, for example, those determined by diesel motors or water turbines have remarkable post-type rotors because of the accompanying reasons :
(a) The notable field poles would cause an over-the-top windage misfortune whenever driven fast and would will in general produce noise.
(b) Salient-shaft development can't be made sufficiently able to withstand the mechanical worries to which they might be oppressed at higher speeds.
- Since a recurrence of 50 Hz is required, we should utilize a large number of poles on the rotor of moderate-speed alternators.
- Low-speed rotors dependably have a huge measurement to give the fundamental space to the poles.
- Thus, notable post-type rotors have substantial breadths and short pivotal lengths.
(ii) Non-salient type
- In this sort, the rotor is made of a smooth strong produced steel outspread chamber having various spaces along the external outskirts.
- The field windings are installed in these spaces and are associated in arrangement with the slip rings through which they are invigorated by the d.c. exciter.
- The areas shaping the poles are generally left un-slotted as appeared in Fig. 22.3.
- Unmistakably the poles framed circular segment non-notable i.e., they don't extend out from the rotor surface.
High-speed alternators (1500 or 3000 r.p.m.) are driven by steam turbines and use non-striking sort rotors because of the accompanying reasons :
(a) This kind of development has mechanical heartiness and gives the silent task at high speeds.
(b) The transition conveyance around the fringe is about a sine wave and subsequently a superior e.m.f. the waveform is gotten than on account of remarkable shaft type.
- Since steam turbines keep running fast and a recurrence of 50 Hz is required, we need a few poles on the rotor of rapid alternators (additionally called turboalternator).
- We can utilize no under 2 poles and this fixes the most astounding conceivable speed.
- For a recurrence of 50 Hz, it is 3000 r.p.m. The following lower speed is 1500 r.p.m. for a 4-shaft machine.
- Subsequently, the turboalternator has 2 or 4 poles and has Small breadths and long pivotal lengths.