Digital Relay
A digital relay is an electronic device that uses digital circuitry to perform the functions of an electromechanical relay. Digital relays use microprocessors and other digital components to detect and respond to electrical signals and can offer advanced features such as programmability and communication capabilities. They are commonly used in power systems, industrial control systems, and other applications where precise control of electrical circuits is required.
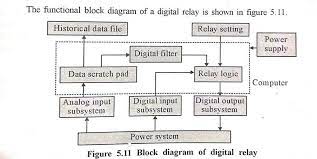
Digital Relay Block Diagram
The power supply unit provides the necessary power to the whole relay from the power system required inputs are applied to the analog input subsystem and to the digital input subsystem. According to the relay setting the relay logic provides the output to the digital output subsystem. The historical data file is used to store the previous records of the digital relay. As the desired output from the digital relay is received by the circuit breaker, the circuit breaker performs the required operation. For a three-phase system, the block diagram of the digital relayThe Digital relay that is in use for protection consists of the following subsystems:
(a) Analog input subsystem
(b) Digital input subsystem
(c) Digital output subsystem
(d) A processor along with RAM (called Data Scratch Pad), main memory (Historical data file), and power supply unit.
The relaying voltages at 110V or 50V and currents at 5A or 1A are first passed through an isolation transformer. Relay settings are stored in the EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory).
The relaying program will be located in the ROM (Read Only Memory) and the RAM (Random Access Memory) will be used for storing sampled quantities and intermediate products are the relaying algorithm.